Melons grown in central Russia are difficult to compare with Central Asian, but with proper agricultural technology they grow quite good, and often no less fragrant. Of course, the sun is not enough, because in many places melons are planted only in the greenhouse, but this does not stop enthusiasts.
Melon variety selection for central Russia
In central Russia, with guaranteed success, not many varieties of melons can be grown. The most traditional ones, which are always “on the ear”, are Altai and Kolkhoznitsa. However, the range is currently not limited to these well-known representatives. At the same time, when choosing a variety for a region not too warm, one must pay attention to whether it is zoned for cultivation in such a climate. Perhaps you can plant the variety you like, but only in the greenhouse.
Melon is slowly moving north, as new varieties and hybrids are constantly appearing, resistant to the vagaries of the weather and not requiring a long summer. Therefore, in recent decades, this culture is engaged in the Bryansk, Kaluga, Ivanovo, Nizhny Novgorod regions.

Early and mid-late melon varieties are suitable for cultivation in central Russia
In any case, in the middle lane you have to confine yourself to early varieties (in extreme cases, the average ripening period), since the late (and they are often the most delicious) will not have time to ripen here. If you look at the State Register of Breeding Achievements of the Russian Federation, it turns out that in the middle lane it is recommended to grow only one variety - Princess Svetlana. A few more are also suitable for similar climatic conditions, for example:
- Collective farmer,
- Lesya
- Lolita
- Tender.
Of course, gardeners are not limited to official recommendations and plant various varieties and hybrids, especially since their number is growing every year.
Melons for open ground:
- Cinderella is a high-yielding variety, one of the most ripening, gives medium-sized slightly oval yellow fruits (weighing from 1 to 2 kg) of excellent honey taste. The growing season is just over 2 months: 60-72 days pass from seedlings to technical maturity. The variety is resistant to diseases and the vagaries of the weather, intended for fresh consumption: the fruits are stored for no more than 2 weeks;
- Altai - a variety that is almost as good as Cinderella in early maturity, harvesting is possible in mid-summer. Fruits are yellow, elongated, weighing up to 1.5 kg. The flesh is less sweet, but beautiful, pale orange, fragrant. Fruits are almost not stored, intended for quick consumption after removal;
- Assol F1 gives yellow-orange rounded fruits weighing about 1 kg. The pulp is very juicy, sweet, fragrant, colored in greenish color. The growing season is from 80 to 90 days. Productivity - up to 1 kg / m2. Melons are stored for about 7 days, the variety is characterized by high resistance to disease;
- The collective farmer is a well-known variety with a medium maturity, grown in most of our country since 1943, with a growing season of 73 to 95 days. The fruit is an ideal ball weighing about 1 kg, yellow-orange color, smooth. The pulp is almost white, sweet, juicy. Appreciated for its excellent taste and high yield, as well as the ability to transport over long distances. The disadvantage of the variety is its low resistance to many diseases;
- Lesa gives larger fruits, weighing more than 2 kg, yellow-orange in color, oval in shape. The pulp is tender, oily, from white to cream color. It ripens in 60-85 days. The aroma is ordinary, inherent in most varieties of melon, the taste is good. The variety is resistant to most diseases and extreme droughts, high yielding.
Photo gallery: melon varieties for open ground

- Cinderella - an early ripening honey melon

- Altai melon is almost not stored, it is eaten directly from the garden

- Assol is not very beautiful on the outside, but tasty

- Melon Kolkhoznitsa - an old, time-tested variety

- Melon Lesya withstands dry weather
Varieties for growing in greenhouses:
- Princess Svetlana. From germination to harvesting takes about 3 months. The fruits are spherical, almost white, weighing about 1.5 kg. The pulp is tender, juicy, orange in color, excellent in taste, with a strong aroma. Fruits are stored for 2.5-3 weeks, normally tolerate transportation;
- Lada ripens 3 months after emergence (before technical maturity it takes 74-96 days), fruits weighing 1.5 to 2 kg, orange, round, very sweet. The flesh is light cream in color. The variety is disease resistant, melons do not crack, the presentation is excellent;
- Titovka is one of the most early ripening varieties; the growing season is 55-70 days. Fruits of orange color, slightly elongated, their size is very diverse: both miniature specimens and melons weighing up to 3.5 kg can be simultaneously present on the bed. The pulp is pure white, fleshy, tasty. Disease resistance at an average level;
- Krinichanka is another representative of very early varieties: the first melons ripen 70 days after emergence. Fruits are round-oval, medium size (about 2 kg), yellow-orange. The pulp is very sweet, variable in color (from greenish to cream). The use of the greenhouse does not affect the ripening speed: the variety can grow with a lack of natural light;
- Scythian gold F1 is an early ripe hybrid, the first fruits ripen in 75-80 days, they are round, small (about 1 kg), yellow. The pulp is sweet, aromatic, tender, very juicy. The presentation is good. The hybrid is famous for its high productivity and good pain tolerance.
Photo gallery: melon varieties for greenhouse cultivation

- Princess Svetlana is easily recognizable by melon coloring

- Melon Lada has a very sweet flesh

- Melon Titovka - ultra-mature variety

- Melon Krinichanka is able to ripen in low light

- Scythian Gold Melon - a high-yielding hybrid for greenhouses
General requirements for growing conditions
Melon needs a lot of heat and sun, which must be considered when choosing a place for a bed. It withstands the most severe heat and very arid weather, since it is able to extract moisture from the deep layers of the soil, but in a humid climate it is not healthy.
The roots go deep into the ground to 1 m or more, although this seems incredible when looking at plants of a very medium size.
Melons feel good on light hills, because excess water does not accumulate there, in the presence of which most varieties quickly become ill. However, these elevations must be reliably protected from cold winds.
The composition of the soil is of great importance: melon does not grow anywhere. She loves light soils in structure: acid-neutral loams are the best option. It is necessary to add a lot of sand to the clay soil, and carefully acidize the acidic soil. The best predecessors are cabbage, cucumbers, peas, garlic, onions. It is undesirable to plant melons after any melons, tomatoes and carrots.
In connection with the requirement of good lighting, they try to grow melons mainly in open ground: the walls of even the best greenhouses absorb a significant amount of sunlight. However, in the middle lane, many gardeners are forced to plant the crop in the greenhouse, since the risk of not ripening in the garden is very high: the summer is different.

Melon needs a lot of space for normal growth
In the central regions, only the very ripe varieties can be grown directly into the soil by sowing, in most cases seedlings have to be prepared. And even at first they keep her in the gardens under light film shelters, removing them no earlier than June 10th.
Historical records show that in the Moscow region melons were planted about 500 years ago, using warm manure beds in greenhouses for this. They are prepared in advance using good doses of organics, covered with a dark plastic film in which holes are made. Melon seedlings are planted in them, without removing the film for the whole summer, and in case of cooling, they are covered with non-woven materials.
Video: growing a melon on a high bed
Growing seedlings
Melon seedlings in a city apartment feel comfortable: there is enough heat, and if there is no sunny window sill, you can highlight with lamps. If there is a greenhouse, seedlings can be prepared in it.
The timing
When calculating the timing of the start of seedling cultivation, you need to know that it will be planted in a permanent place at least 30 days old. True, when using peat pots or tablets, this period can be reduced, since such a transplant does not affect the root system, but you should not rush into this matter. Thus, you need at least a month and even a week for seed germination. And since transplanting to the garden in the central regions before the beginning of summer is risky, it turns out that the optimal time for sowing seeds in pots is the end of April.
Sowing seeds should be done no later than mid-May, so melon is a "short day" culture. This term describes the biological characteristics of the plant: for normal flowering, it does not need the longest daylight hours. In the center of Russia in June the sun shines for 17 hours, and for a melon it is a lot. In such a situation, less flowers are formed, they are pollinated worse. Hence the dilemma: on the one hand, temperature conditions are requested to be sown, but on the other, the melon should bloom as early as possible, at least in early June.
Early March sowing in the middle lane is also useless: where to plant seedlings in April? It's still cold in the greenhouse. On the March windowsill, plants will be frail. Therefore, the period for sowing is unambiguous: the last of April or the first of May. If it’s already warm, you can put seedling pots in the greenhouse, if spring has not been set - at home, on the windowsill.
Sowing seeds for seedlings
It is better to sow melons for seedlings immediately in separate cups, and ideally in peat pots: planting in a box with subsequent diving is possible, but undesirable, melons are painfully transplanted. The capacity of the pot is from 200 ml. It is filled with a soil mixture of any composition, but the soil obtained by mixing the components should turn out to be light and fertile. The optimal composition is equal shares of garden soil, sand, peat and humus.

It’s better to plant melon seeds in peat pots, as the crop is not very good for transplanting
As for the seeds, it is best to buy them in a safe place. If you take them from a tasty melon purchased for food, it is not a fact that success will be guaranteed: a hybrid can get caught, and their seeds give shoots of incomprehensible varieties, and instead of the expected fruits, you may have to try something grassy in late summer. In addition, bought melons could be brought from far away and not at all fit into the local climate.
To collect seeds from independently grown fruits, you need to choose the most ripe and largest melons.
Annual seeds should not be used: they give a lot of empty flowers, you can not get a crop at all. The best seeds are from 3 to 6 years old. If the origin is unknown, it is worth disinfecting them in the usual way: hold for half an hour in a dark solution of potassium permanganate, then rinse well with water. In the central areas, the melon seeds are necessarily hardened by placing in the refrigerator after disinfection at night.
Some summer residents sprout seeds before sowing, but this procedure does not play a big role: usually even dry seeds germinate well.

Melon seeds are similar to cucumber, easy to work with
In each pot, moistening the soil, sow 2-3 seeds to a depth of about 2 cm, then remove extra seedlings. It is advisable to sprinkle the crops with a layer of clean, dry sand. Before germination, the pots are kept warm by covering them with glass or a transparent film. Immediately after the appearance of the shoots (after about a week), the temperature should be lowered to 16-18 ° C for several days, but at the same time they should be in good light conditions.
Seedling Care
When the seedlings grow to 2-3 cm, it is necessary to leave only one plant in each pot. The optimum temperature when growing melon seedlings is about 20 ° C during the day and 15 ° C at night. Watering under the root, in moderation (1 time in 2 days). Daylight hours for seedlings should last about 12 hours. If the windowsill is facing north, it is advisable to add a backlight to the natural light.
A normal incandescent lamp will work for a melon, but with special lamps or even with luminescent spectral composition is much closer to sunlight.
After the appearance of two real leaves, seedlings need to be fed. To do this, you can use weak solutions of any complex fertilizers, although melon reacts much better to natural ones. Of course, it is not worth recommending to breed mullein in the apartment, but now there are also ready-made extracts of organic fertilizers on sale. If the seedlings are delayed, after 2 weeks, top dressing must be repeated.
Already in the third week of life, seedlings begin to be little by little brought to the balcony and accustomed to fresh air. At first it should be half-hour "walks", gradually increase the time. Seedlings at least 4 weeks old, having a thick sturdy stalk and 5-6 healthy true leaves, are ready for transplanting.

Ready to plant seedlings is a viable plant
Transplanting seedlings into the garden
In the beds without shelter, melon seedlings can be transplanted when daytime temperatures of about 15-20 are establishedaboutC, and night - not lower than 6aboutC. At the end of May, such a regime usually occurs in the climatic zone of the middle zone, but there still remains the danger of night frosts. Therefore, if you can’t wait another week, the seedlings must be planted under a temporary film shelter.
If the seedlings are planted, and the frosts have come, it is imperative to install a portable shelter: even zero temperature is destructive for a melon.
Planting scheme implies not only sufficient space for each bush, but also the possibility of caring for them: melons have to be watered, fed, and form bushes. To do this, you need a free approach to them. Most often, a horizontal landing is used with distances between rows of at least 70-90 cm, and between bushes in a row - from 50 cm. If there is enough space on the bed, melons are planted according to the scheme 120 x 60 cm.
Sometimes a kind of flowerbed is made of melons: in a one and a half meter circle, one plant is placed in the middle and 5-6 on the edges of the circle.
Planting melon is simple, you must follow these steps:
- Dig deep holes, add about 2 kg of humus or compost to them; mix the fertilizer with the ground and water it well, then dig a hole with a scoop on the size of the pots with seedlings.

Fertilizers with soil must be mixed very carefully.
- Pour seedlings several hours before planting with clean water.
- From plastic pots, very carefully get the plants with a soil lump, peat pots are planted whole.

Seedlings from pots are removed very carefully so as not to damage the roots
- Plant melon in the holes at the same level as it grew at home or even a little higher: you can not deepen the plants.

It is not allowed to bury plants
- Pour seedlings from a mug without washing away the ground, making sure that the bush does not fall too low.
- Mulch the plantings with a thin layer of dry clean sand and temporarily cover with a spanbond.
If the weather is really warm, you can do without shelter, but protection from bright sunlight is still needed; in such weather it is more useful to mulch the bushes with mowed grass.
Video: growing melon seedlings
Sowing melon seeds in the garden
In the middle lane, sowing melons directly into the garden is rarely done.Since the deadline is mid-May, when warm weather has not yet been established, there is a great risk that the sprouts will die and a temporary film cover is absolutely necessary. But to sow melon in the greenhouse in early May is already quite possible.
Sowing melon in the open ground
Since the melon is not sown very early, the garden can be prepared in the spring, but more often they try to do it in the fall. The site is dug up on a bayonet shovel, making 1 m2 a bucket of well-rotted manure or compost. Shortly before sowing, sprinkled on a bed of wood ash (up to 1 liter per 1 m2), level the soil with a rake, and preferably with a cultivator.
Sowing seeds is possible a little earlier than planting seedlings, that is, after May 20: the earth at this time is already quite warm. While the seeds hatch and germinate, real warmth must come. The sowing pattern is similar to that when planting seedlings: the minimum distance between holes in a row is 50 cm, between rows - 70 cm.
Procedure:
- They make small pits with a scoop, add 1 tbsp to them. ash and a pinch of azofoska, mix and pour with warm water.

Azofoska is a valuable mineral fertilizer, but for a melon it is necessary to take very little
- In each hole to a depth of about 3 cm, 2-3 melon seeds are placed.

2-3 seeds are very easy to take: they are quite large
- Sprinkle seeds with earth, ram, sprinkle with clean sand.
- If the warm weather has not been reliably established, cover the bed with a spanbond.
After 10-12 days (and if it is very warm, then early) shoots will appear. As soon as it is clear which of them are stronger, one sprout is left in each nest.
Melons coexist well with corn, beans, radish, any odorous herbs. You should not have nearby potatoes and cucumbers. There should not be any trees that create strong shading. Often holes with melons alternate with planting watermelons.
Sowing seeds in a greenhouse
Melons are grown in unheated greenhouses: another option is unsuitable, because this culture needs sunlight, and heated greenhouses make sense in winter and early spring. To grow melons, you need to choose high greenhouses with a height of at least 2 m, otherwise the use of their areas will be too wasteful. Each plant needs a lot of space, so melons in the greenhouse culture are grown vertically, with a garter to the built strong trellises.
So that the trellis does not occupy the main area of the greenhouse, they try to place them along the side walls. Accordingly, the beds for melons are prepared no further than 50 cm from the walls, and most often they build ridges up to 20 cm high, in which single-row sowing is carried out. Between the holes, they try to maintain a distance of at least 40 cm.

Melons are planted at the wall of the greenhouse, they are free there
The beds are prepared in advance, but in the greenhouse it is often necessary to completely replace the soil. This is especially important if, in previous years, gourds grew at the selected place. The best soil for the greenhouse, which is supposed to grow melons, consists of lowland peat and fine sand (3: 1), to which chalk and azofoska (300 and 40 g per 1 m are added for deoxidation)2 respectively). If there is no peat, but ordinary garden land is used, it is fertilized in the same way as in open beds.
Sowing melons in the greenhouse is possible in early May. The technique is no different from sowing in the garden, only it is not necessary to cover the bed. Shoots will appear in 7-10 days, and for the first time it is desirable to lower the temperature in the greenhouse a little (to 16-18aboutFROM).
It is especially important that the greenhouse does not get hot at night.
Melon Care
Plant care consists of the usual gardening activities: watering, cultivating, fertilizing. In addition, melon bushes have to be formed so that they can stretch the crop: as a rule, too many fruits are tied, and extra foliage is not needed. Caring for melon in the greenhouse and outside is somewhat different.
Outdoor melon cultivation
Melon does not require frequent watering: they are needed until the plant develops, and then - only in the driest weather. Before setting fruit, as a rule, melon is watered once a week. It is important that the water is not too cold: in the evening it warms up well in barrels in the sun. With the advent of fruits, watering is carried out less and less, and when the melons grow to the size of a fist, they completely stop.
While the whips have not filled all the free space, after rains or watering, shallow cultivation is carried out with the removal of weeds. As soon as the side shoots begin to appear, the melons lightly spud. Feed them:
- 10-15 days after transplanting,
- with the advent of the first flowers,
- at the very beginning of fruit loading.
Mineral fertilizers should not be used, it is better to use mullein infusion with the addition of ash. If in the process of fruit growth it turns out that only one of them increases in size, top dressing should be added.
Competent pruning of melon, consisting of pinching shoots, removing stepsons and excess fruit, is of great importance. As soon as it becomes clear that the seedlings have successfully taken root and began to grow, pinch the main shoot at its very top. After a few days, the side shoots begin to grow, but there are too many of them, and you need to choose the two strongest ones, and remove the rest. Growing stepchildren are systematically broken down.

Any melon pruning scheme involves limiting the number of shoots and fruits
In most hybrids, the bearing fruit is different, and they, on the contrary, pinch lateral shoots after the formation of three leaves on them, because the main crop will form on the main stem.
Even with the most careful care, the melon bush will not feed more than 6 fruits (and the largest ones - only 2-3 pieces), so the rest will have to be sacrificed. Since melon plants are rarely displayed on trellises in the open ground, it is worthwhile to place small plywood or planks under each fruit so that the melons do not lie on bare ground and do not rot in case of rain.
Special events in the greenhouse
In the greenhouse, artificial pollination is added to all the above activities. In the fresh air, flying insects do this, which rarely appear in protected ground. Of course, if the greenhouse is systematically ventilated (and it is necessary to do this), then the bees can fly into it, but in this case the process cannot be left to chance. Therefore, the owner himself must pick several male flowers (those on a thin long stalk), cut off the petals from them and touch them several times on the inside of the female flowers. This should be done on the very first day or two after the male flowers bloom until pollen has circled.
Another feature of caring for melons in a greenhouse is growing them on a trellis to save space. It can be any stable vertical supports to which melon whips are tied (they themselves will not climb up). Since the ripening melons may fall, they (after reaching the size of the average apple) are placed in any suitable nets that are tied to the trellis.

The mesh is needed so that the melon does not fall and break
In the greenhouse, pruning is carried out minimally: the extra fruits there usually do not tie or die very quickly. It is important not to overfill the water: excessive humidity in the greenhouse is fraught with the occurrence of diseases.
Video: melons in the greenhouse
Diseases and Pests
Most modern varieties of melons are resistant to diseases and pests, and often summer residents do not pay attention to this moment at all. However, there are ailments that pose a danger:
- powdery mildew first appears on the leaves, then passes on to the stems. A sign of appearance are small white spots, similar to flour. Leaves soon turn yellow and fall. If the matter has gone far, the fruits are amazed. Prevention of the disease consists in the careful collection of all plant residues and compliance with agricultural technology. In case of infection, colloidal sulfur preparations help;

Powdery mildew is hard not to recognize: the leaves are as if sprinkled with white coating
- olive spotting appears on the leaves in the form of brownish spots, on the stems in the form of ulcers. If it comes to the fruit, spots appear on them, quickly turning into dark ulcers. Prevention and fight against spotting is the same as with powdery mildew. In addition, with severe infection, the use of Bordeaux fluid is possible;
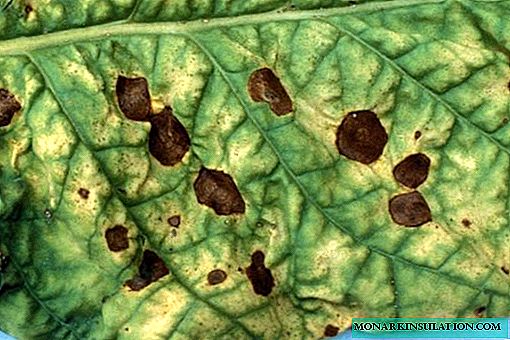
When olive spotting leaves are covered with dark spots
- Anthracnose appears in the form of large yellowish spots on leaves, stems and fruits. Soon spots turn pinkish. Especially often, the disease occurs with high humidity of the soil and air, which is mainly observed in greenhouses. If the disease progresses, the plants die. With proper care of the plantings, the ailment is rare, and with its appearance, in addition to sulfur preparations, a 1% solution of Bordeaux mixture can help.

With anthracnose, pinkish patches appear on the fruits
Melon aphids and spider mites are the most dangerous pests of melon. They do not attack the fruits, but severely damage the leaves, sucking juices out of them. Since severe damage to the leaves leads to their death, the plants do not receive the right amount of nutrients and may also die as a result. Prevention of pest attack is a strict alternation of crops in the garden and timely weed control. When a significant number of insects appear, it is necessary to use karbofos or a strong soapy solution.

Melon aphid sucks plant sap
Among the large pests, birds are also worth mentioning, especially the raven, which hatch a significant part of the ripe crop.
Harvesting and storage
In the middle band, melons can be expected from late July. For a more even ripening, they are turned over if possible with different sides to the sun. It is much easier to determine the maturity of a melon on a bed than a watermelon: at the time of maturity, they acquire a characteristic color for the variety, and in many cases even without cutting exude a pleasant aroma. If the melon has not ripened a bit, it's okay: its ripening will continue during the first time during storage. But absolutely unprepared fruits are not worth picking: they will not reach ripeness, but simply disappear. You can’t leave melons in the garden for longer than the prescribed time: when re-ripening, many varieties crack, after which they are quickly affected by birds and various insects.
Melons are cut together with a peduncle 4-5 cm long. They must be transported to the storage place carefully, on a soft litter, protecting from shock. It is advisable to store them separately from other fruits and vegetables. Most varieties grown in the central regions are not subject to long-term storage, but it is worth knowing that late melons can be stored under the right conditions for up to six months. This is, first of all, low temperature (1-3 ° C) and not very high humidity (70-80%).
Growing a good melon in the middle lane is not easy: most varieties do not have time to ripen. But among the ripening there are varieties and hybrids that give very tasty fruits. The summer resident should be patient, since it is desirable to grow a melon through seedlings, and in the garden to systematically care for it. Under such conditions, in the suburbs it is quite possible to please yourself with aromatic fruits.





























